|
I am a Research Scientist at Sea AI Lab, based on Singapore, working on Research Interests:
I earned my Ph.D. and Bachelor's degree in Computer Science from Harbin Institute of Technology advised by Professor Wanxiang Che. I worked as a research intern at Microsoft Research Asia with Dr.Jian-Guang Lou and at National University of Singapore with Professor Min-Yen Kan. Email / Google Scholar / LinkedIn / Resume / Github / Twitter |

|
|
|
|
Longxu Dou*, Cunxiao Du*, Shenggui Li*, Tianduo Wang, Tianjie Zhang, Tianyu Liu, Xianwei Chen, Chenxia Tang, Yuanheng Zhao, Min Lin Project, 2025 
Work in progress — exciting updates coming soon!
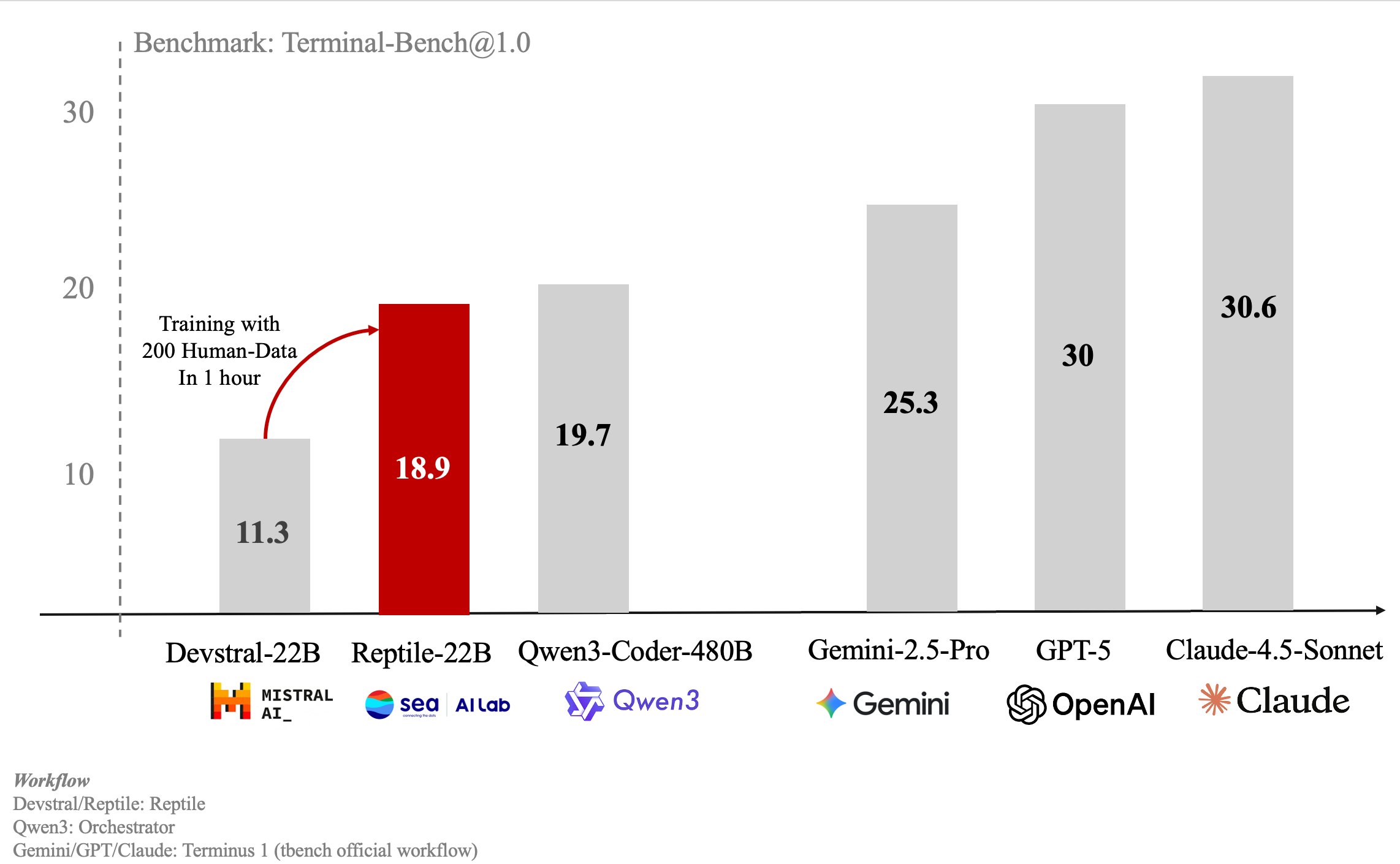
Reptile is a Terminal Agent that enables interaction with an LLM agent directly in your terminal.
The agent can execute any command or custom CLI tool to accomplish tasks, and users can define their own tools and commands for the agent to utilize.
Compared with other CLI agents (e.g., Claude Code and Mini SWE-Agent), Reptile stands out for the following reasons:
• Terminal-bench: 11.3% → 18.9% • SWE-Bench-Verified: 18.6% → 32.8% |
|
Longxu Dou*, Qian Liu*, Fan Zhou*, Changyu Chen*, Zili Wang, Ziqi Jin, Zichen Liu, Tongyao Zhu, Cunxiao Du, Penghui Yang, Haonan Wang, Jiaheng Liu, Yongchi Zhao, Xiachong Feng, Xin Mao, Man Tsung Yeung, Sailor2 Team Report, 2025  Slides
Slides
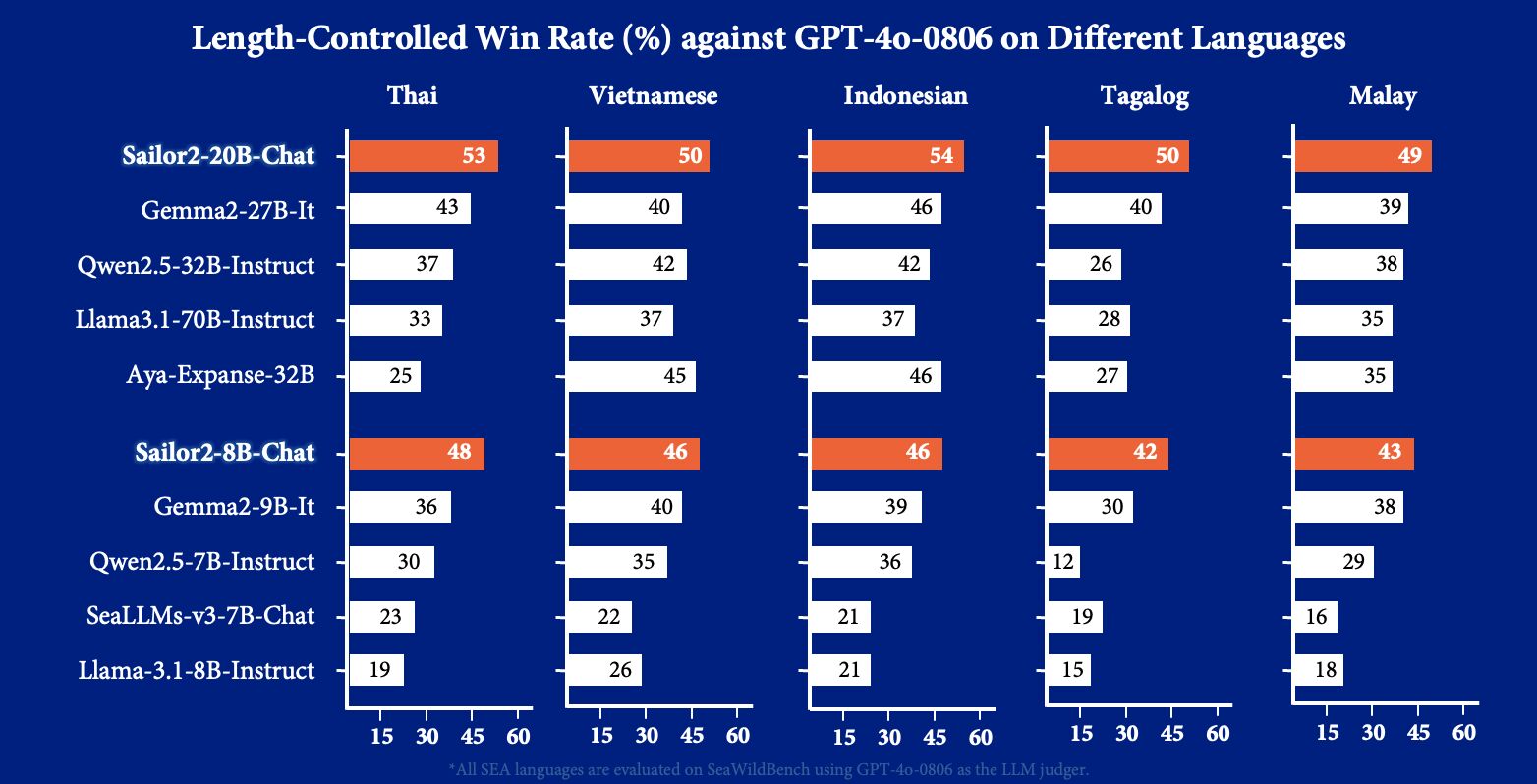
Sailor2 is a community-driven project delivering state-of-the-art multilingual language models in three scales - 1B, 8B, and 20B parameters. Released under the Apache 2.0 license, these models specialize in South-East Asian (SEA) languages, making advanced models more accessible across the region. Building upon the foundation of Qwen2.5 , Sailor2 is continually pre-trained over 500B high-quality tokens to support 15 languages, including English, Chinese, Burmese, Cebuano, Ilocano, Indonesian, Javanese, Khmer, Lao, Malay, Sundanese, Tagalog, Thai, Vietnamese, Waray. • Sailor2-20B-Chat achieves a nearly 50% win rate against GPT-4o-0806 on SeaWildBench, showcasing GPT-4o-level performance in local chat scenarios on South-East Asian Languages. • Over 300K downloads since released |
|
Longxu Dou*, Qian Liu*, Guangtao Zeng, Jia Guo, Jiahui Zhou, Xin Mao, Ziqi Jin, Wei Lu, Min Lin EMNLP Demo, 2024  Slides
Slides
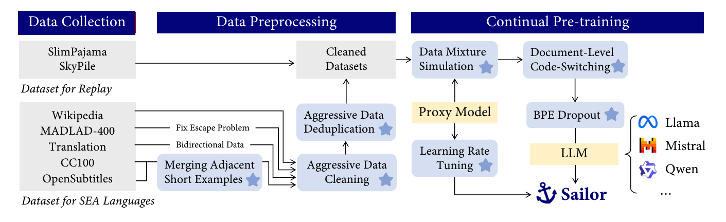
Sailor is a family of open language models ranging from 0.5B to 14B parameters, tailored for South-East Asian (SEA) languages. These models are continually pre-trained from Qwen1.5, a great language model for multilingual use cases. From Qwen1.5, Sailor models accept 200B to 400B tokens, primarily covering the languages of English, Chinese, Vietnamese, Thai, Indonesian, Malay, and Lao. The training leverages several techniques, including BPE dropout for improving the model robustness, aggressive data cleaning and deduplication, and small proxy models to optimize data mixture. • Over 200K downloads since released. |
|
Longxu Dou Tool, 2024 
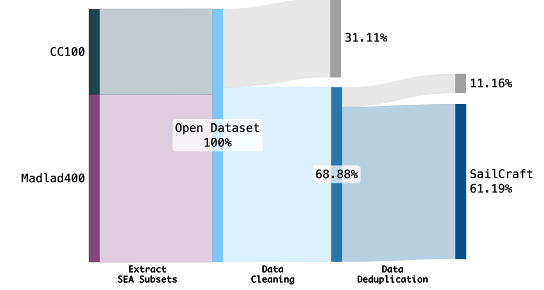
The full data processing script used in developing our Sailor models. The repo provides an end-to-end data processing pipeline for LLM training. With this codebase, you can clean your own dataset with: (1) Get filtered data counts after each processing stage. (2) Easily configure language-specific cleaning rules (we support Arabic, Bengali, Catalan, Spanish, Basque, French, Hindi, Portuguese, Urdu, and optimize for English, Indonesian, Vietnamese, Chinese, Thai, Lao, Malay). (3) Investigate what data was removed at each processing stage. |
|
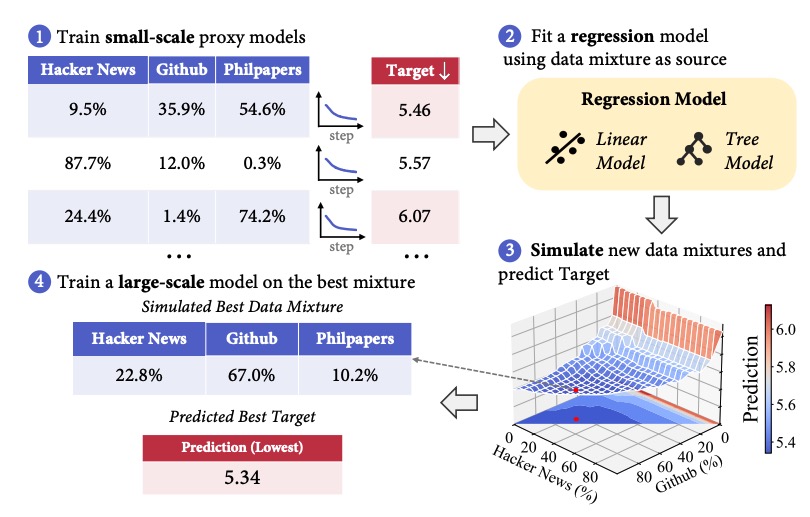
Qian Liu, Xiaosen Zheng, Niklas Muennighoff, Guangtao Zeng, Longxu Dou, Tianyu Pang, Jing Jiang, Min Lin ICLR (Spotlight) , 2025 
The data mixture for large language model pre-training significantly impacts performance, yet how to determine an effective mixture remains unclear. We propose RegMix to automatically identify a high-performing data mixture by formulating it as a regression task. RegMix trains many small models on diverse data mixtures, uses regression to predict performance of unseen mixtures, and applies the best predicted mixture to train a large-scale model with orders of magnitude more compute. |
|
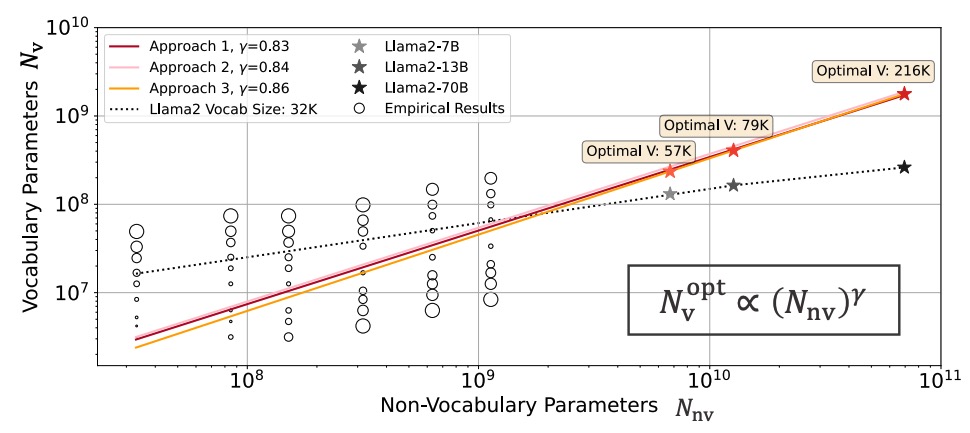
Chaofan Tao, Qian Liu#, Longxu Dou#, Niklas Muennighoff, Zhongwei Wan, Ping Luo, Min Lin, Ngai Wong NeurIPS, 2024 
Research on scaling large language models (LLMs) has primarily focused on model parameters and training data size, overlooking the role of vocabulary size. We investigate how vocabulary size impacts LLM scaling laws by training models ranging from 33M to 3B parameters on up to 500B characters with various vocabulary configurations. We propose three complementary approaches for predicting the compute-optimal vocabulary size: IsoFLOPs analysis, derivative estimation, and parametric fit of the loss function. Our approaches converge on the conclusion that the optimal vocabulary size depends on the compute budget, with larger models requiring larger vocabularies. |
|
Design and source code from Jon Barron. |